Endoscopy centres are specialized medical facilities dedicated to performing endoscopic procedures, which involve the use of an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity in the body. These centres play a crucial role in diagnosing, monitoring, and treating various gastrointestinal (GI) disorders and other conditions. This article delves into the function, importance, procedures, and advancements of endoscopy centres, highlighting their contribution to modern medicine.
What is an Endoscopy?
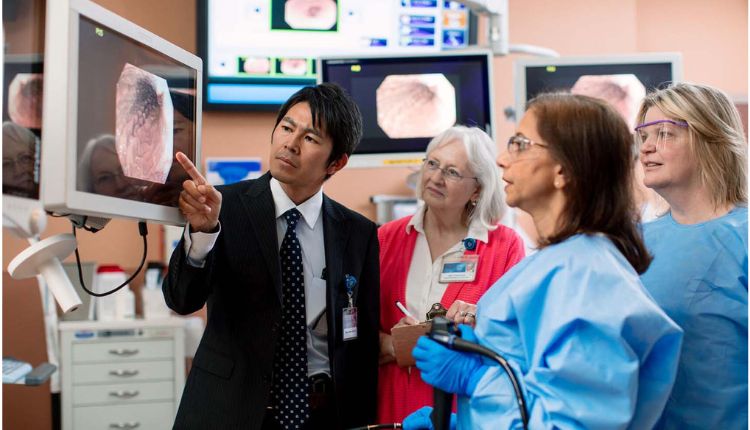
Endoscopy Centre is a minimally invasive diagnostic medical procedure that allows doctors to view the inside of a patient’s body without making large incisions. An endoscope, a flexible tube with a light and camera attached, is inserted into the body through natural openings such as the mouth or anus or through small incisions. The camera transmits images to a monitor, enabling physicians to inspect internal organs and tissues.
Functions of an Endoscopy Centre
Endoscopy centres are equipped to perform various diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, including:
- Gastroscopy: Examination of the upper GI tract, including the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. It is commonly used to diagnose ulcers, gastritis, and cancers.
- Colonoscopy: Inspection of the colon and rectum, primarily for detecting colorectal cancer, polyps, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
- Bronchoscopy: Used to view the airways and diagnose lung conditions.
- Cystoscopy: Examination of the bladder and urethra.
- Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS): Combines endoscopy and ultrasound to obtain detailed images of the digestive tract and surrounding tissues.
Importance of Endoscopy Centres
Endoscopy centres are vital for several reasons:
- Early Diagnosis: Many conditions, such as cancers and gastrointestinal diseases, can be detected at an early stage, significantly improving treatment outcomes.
- Minimally Invasive: Endoscopic procedures are less invasive than traditional surgeries, leading to quicker recovery times and fewer complications.
- Versatility: They are used for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, such as removing polyps, taking biopsies, and treating bleeding ulcers.
- Patient Comfort: These centres are designed to provide a comfortable environment for patients undergoing potentially anxiety-inducing procedures.
The Procedure
An endoscopic procedure typically involves the following steps:
- Preparation: Patients may need to fast for several hours before the procedure. For a colonoscopy, bowel preparation with laxatives is necessary.
- Sedation: Most endoscopies are performed under conscious sedation, where the patient is relaxed and comfortable but not fully unconscious. General anesthesia may be used for more complex procedures.
- Insertion: The endoscope is gently inserted into the body. For a gastroscopy, it is passed through the mouth, while for a colonoscopy, it is inserted through the anus.
- Examination: The physician examines the internal organs on a monitor, looking for abnormalities.
- Intervention: If necessary, therapeutic interventions such as biopsy, polyp removal, or stent placement are performed.
- Recovery: Patients are monitored as the sedation wears off. They may experience mild discomfort but can usually return home the same day.
Advancements in Endoscopic Technology
Endoscopy has seen significant technological advancements, enhancing the precision, safety, and capabilities of procedures:
- High-Definition Imaging: Modern endoscopes offer high-definition video, providing clearer and more detailed images.
- Narrow Band Imaging (NBI): This technology enhances the visibility of blood vessels and mucosal patterns, improving the detection of abnormal tissues.
- Capsule Endoscopy: A swallowable capsule with a camera allows for the examination of the small intestine, which is difficult to reach with traditional endoscopes.
- Robotic Endoscopy: Robots assist in performing complex procedures with high precision.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms are increasingly being used to assist in diagnosing conditions from endoscopic images, improving accuracy and efficiency.
Safety and Risks
While endoscopic procedures are generally safe, they do carry some risks, including:
- Perforation: Rarely, the endoscope can puncture an organ, requiring surgical repair.
- Bleeding: Particularly if a biopsy or polyp removal is performed, there may be minor bleeding.
- Infection: Although sterile techniques are used, there is a small risk of infection.
- Adverse Reactions: Some patients may react to sedation or have complications due to existing health conditions.